Help ensure patients are ready to treat a severe low with Gvoke HypoPen® (glucagon injection)
GVOKE is contraindicated in patients with pheochromocytoma because of the risk of substantial increase in blood pressure.
See additional Important Safety Information below.

Well Studied
Gvoke Was Evaluated in 2 Phase 3 Trials of Adults With T1D3,4
154 subjects received an injection of Gvoke and 157 subjects received an injection of GEK. A total of 152 subjects received both Gvoke and GEK.
In Study A, mean plasma glucose at time of administration was 44.8 mg/dL for Gvoke and 45.2 mg/dL for GEK. In Study B, mean plasma glucose at time of administration was 47.7 mg/dL for Gvoke and 48.7 mg/dL for GEK.
The Safety and Efficacy of Gvoke® for Children and Adolescents Was Evaluated in a Phase 3, Open-label Study3,7
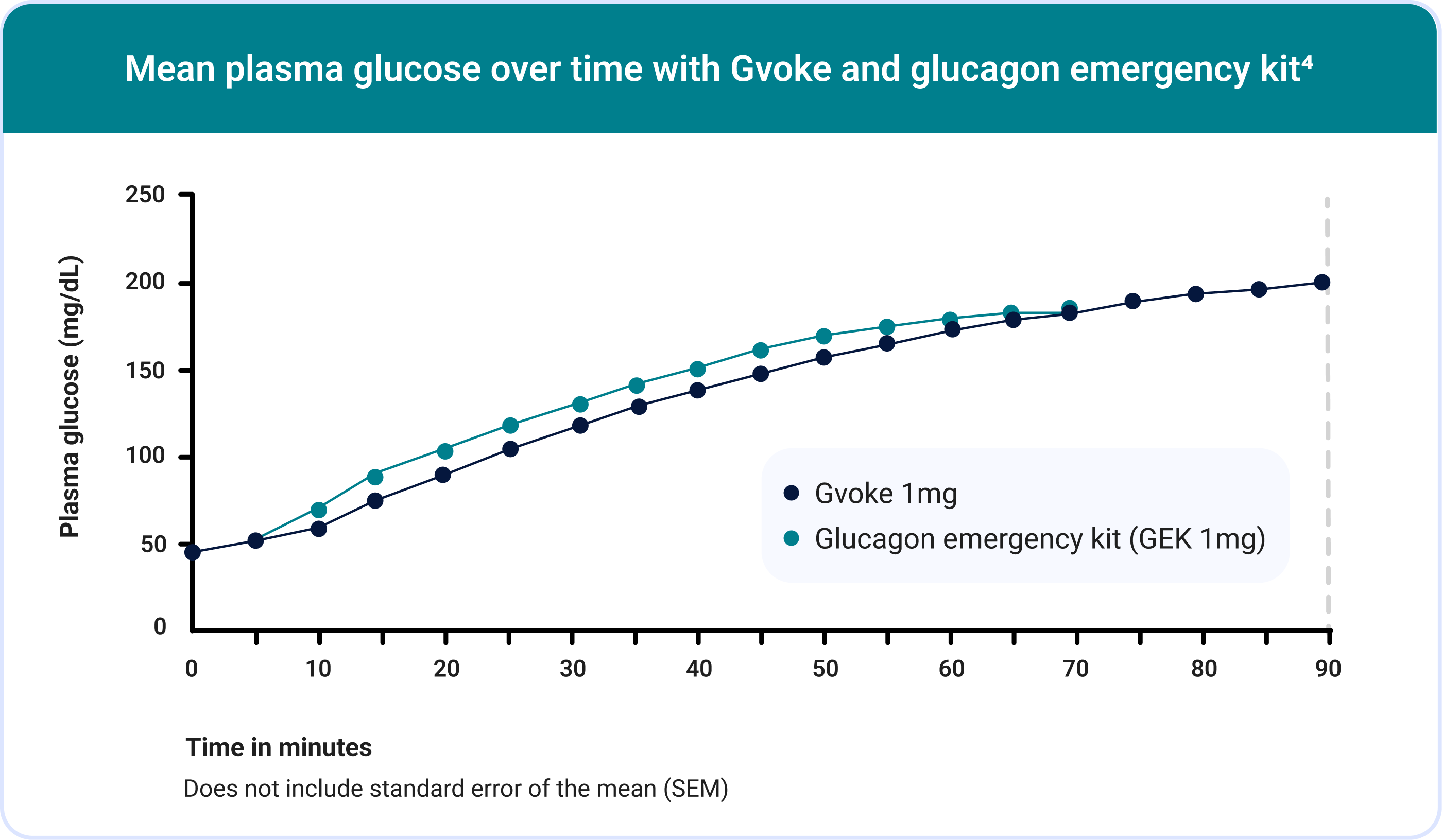
99% (152/154) of adult patients achieved treatment success defined as plasma glucose > 70 mg/dL or an increase ≥ 20 mg/dL from baseline in a pooled analysis of Study A and Study B.3,4
The most common adverse reactions in adults (N=154) were3: nausea (30%), vomiting (16%), injection site edema raised 1 mm or greater (7%), and headache (5%).
Adverse reactions that occurred within 12 hours.
The mean time to treatment success was 13.8 minutes in the Gvoke group.
Works Quickly
Some patients began to feel hypoglycemia symptom relief after a few minutes.4,5†
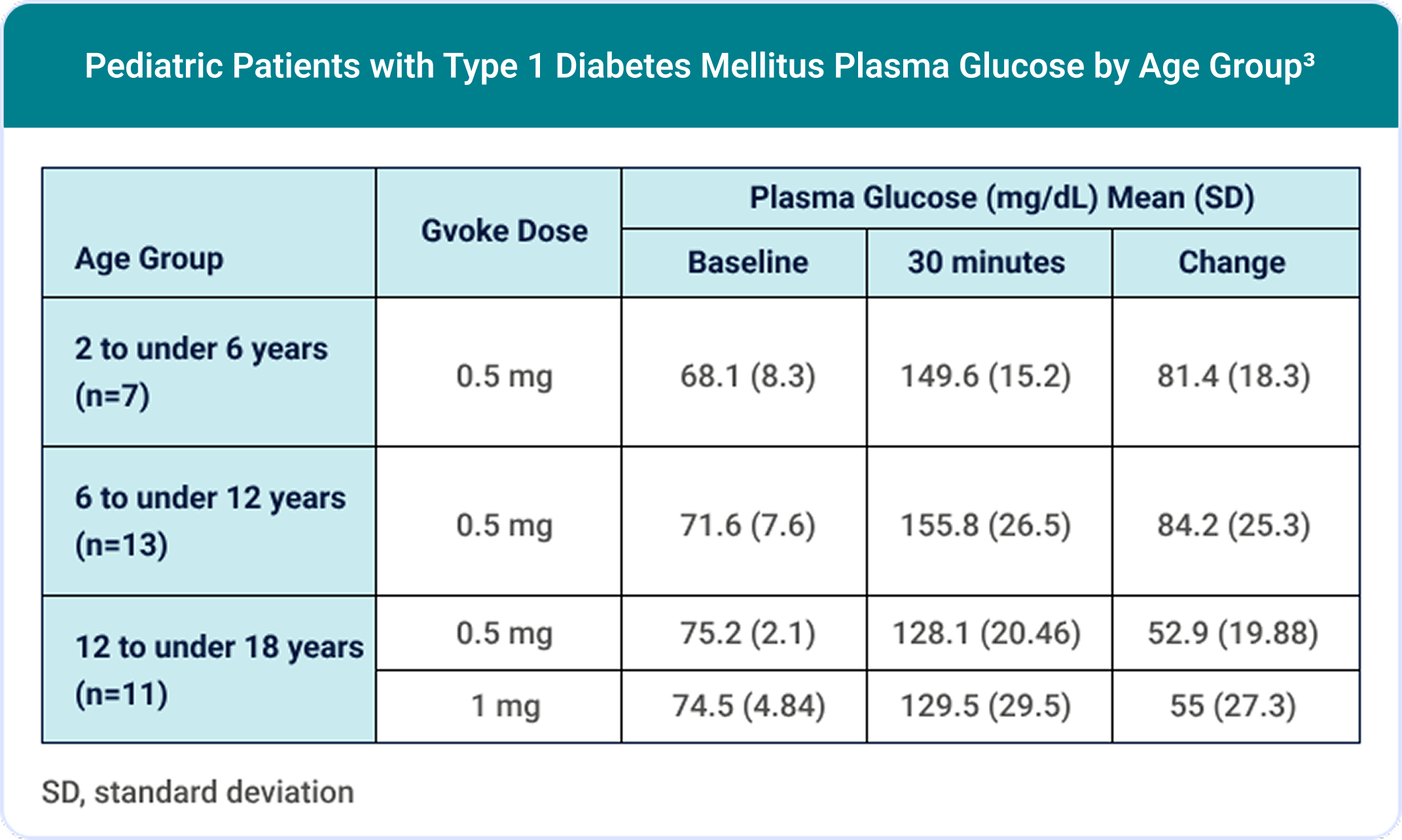
100% (30/30) of pediatric patients achieved a target glucose increase of ≥25 mg/dL.3,7
The most common adverse reactions in pediatric patients (N=31) were3: nausea (45%), hypoglycemia (39%), vomiting (19%), headache (7%), hyperglycemia (7%), abdominal pain (3%), injection site discomfort (3%), injection site reaction (3%), and urticaria (3%).
Adverse reactions that occurred within 12 hours.

Works Quickly
Some patients began to feel hypoglycemia symptom relief after a few minutes.4,5†
Simple to Administer
In the human factors validation study, 99% (74/75) of people were able to successfully administer Gvoke HypoPen under simulated emergency conditions.1
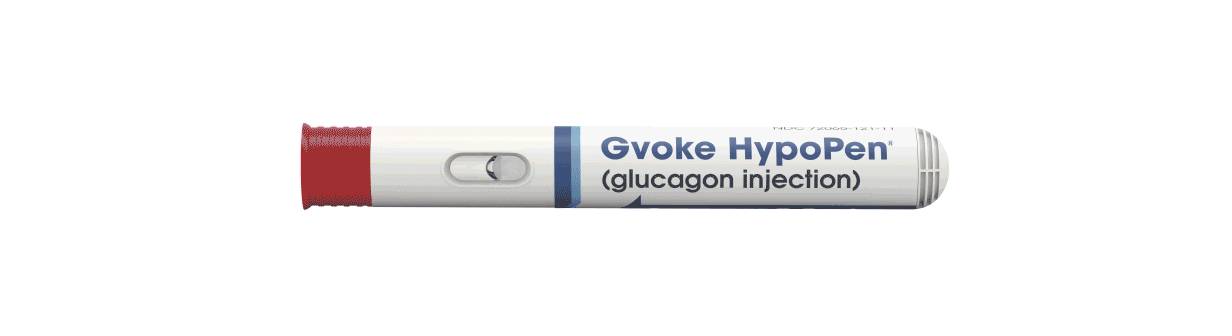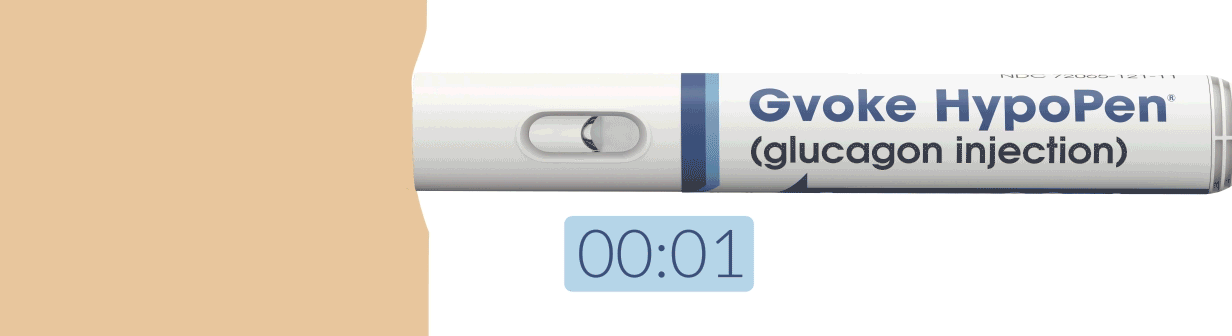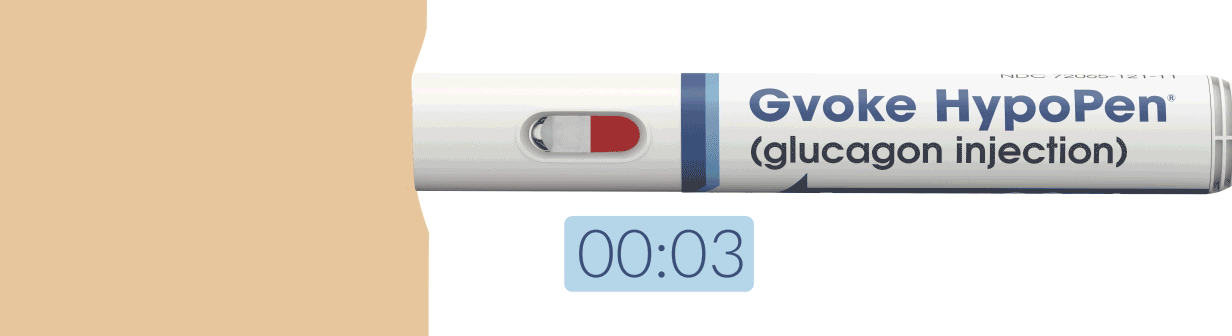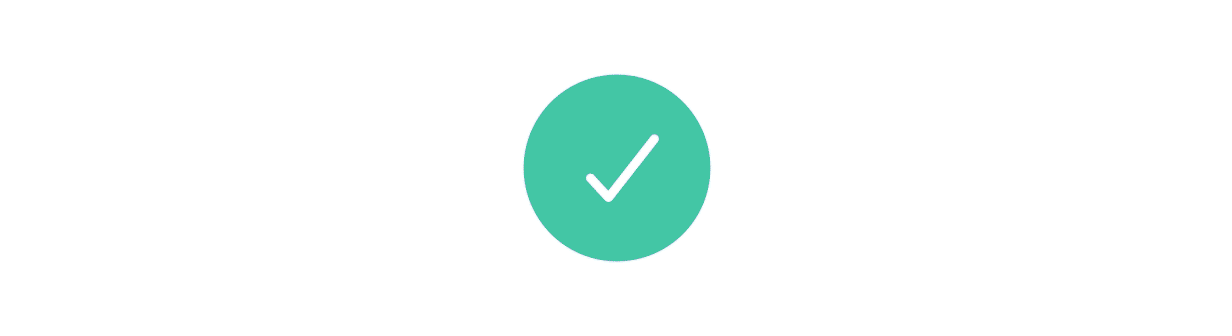
How To Use Gvoke HypoPen in 2 Simple Steps1,6

Understanding Dosages
Gvoke HypoPen comes in two premeasured dosing options.3
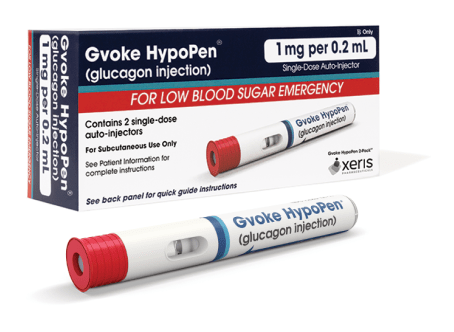
1 mg per 0.2 mL
- For patients ages 12 and older, or children under 12 years old who weigh ≥ 100 lbs
- Lasts 30 months from date of manufacture when stored at room temperature5
0.5 mg per 0.1 mL
- For patients between the ages 2 and 11 who weigh less than 100 lbs
- Lasts 24 months from date of manufacture when stored at room temperature5
Help Patients Save Money on Gvoke HypoPen

Access Financial Support

REFERENCES:
- Valentine V, Newswanger B, Prestrelski S, Andre AD, Garibaldi M. Human factors usability and validation studies of a glucagon autoinjector in a simulated severe hypoglycemia rescue situation. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2019;21(9):522-530. doi:10.1089/dia.2019.0148
- Meyer JM, Devona MC. U.S. Survey investigating gaps between patients and specialists in the treatment of severe hypoglycemia and impressions of the ease-of-use of liquid-stable glucagon for subcutaneous injection. Int Arch Endocrinol Clin Res. 2021; (1):025. doi:10.23937/2572-407X.1510025
- Gvoke [prescribing information]. Chicago, IL: Xeris Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
- Christiansen MP, Cummins M, Prestrelski S, Close NC, Nguyen A, Junaidi K. Comparison of a ready-to-use liquid glucagon injection administered by autoinjector to glucagon emergency kit for the symptomatic relief of severe hypoglycemia: two randomized crossover non-inferiority studies. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2021;9(1):e002137. doi:10.1136/bmjdrc-2021-002137
- Data on file. Xeris Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
- Gvoke HypoPen [instructions for use]. Chicago, IL: Xeris Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
- Buckingham B, Sherr J, Prestrelski SJ, Conoscenti V. Pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, safety, and tolerability of a ready-to-use, room temperature, liquid stable glucagon administered via an autoinjector pen to youth with type 1 diabetes. Pediatr Diabetes. 2022;23(6):754-762. doi:10.1111/pedi.13360
Indication
GVOKE (glucagon) is an antihypoglycemic agent indicated for subcutaneous use for the treatment of severe hypoglycemia in adult and pediatric patients aged 2 years and older with diabetes.
Important Safety Information
- GVOKE is contraindicated in patients with:
-
- Pheochromocytoma because of the risk of substantial increase in blood pressure
- lnsulinoma because of the risk of hypoglycemia
- Prior hypersensitivity reaction to glucagon or to any of the excipients. Serious hypersensitivity reactions have been reported with glucagon, including generalized rash, and anaphylactic shock with breathing difficulties and hypotension
- GVOKE may stimulate the release of catecholamines from the tumor. If patient develops a substantial increase in blood pressure and a previously undiagnosed pheochromocytoma is suspected, 5 to 10 mg of phentolamine mesylate intravenously has been shown to be effective in lowering blood pressure
- In patients with insulinoma, administration of glucagon may produce an initial increase in blood glucose; however, administration may stimulate exaggerated insulin release from an insulinoma and cause hypoglycemia. If a patient develops symptoms of hypoglycemia after a dose of GVOKE, give glucose orally or intravenously
- Patients with insufficient hepatic stores of glycogen may not respond to GVOKE for treatment of severe hypoglycemia. Insufficient hepatic stores of glycogen may be present in conditions such as states of starvation, or in patients with adrenal insufficiency or chronic hypoglycemia
- A skin rash called necrolytic migratory erythema (NME), has been reported post-marketing following continuous glucagon infusion and resolved with discontinuation of the glucagon. GVOKE is not approved for continuous infusion. Should NME occur, consider whether the benefits of continuous glucagon infusion outweigh the risks
- Most common adverse reactions reported in adult patients were nausea, vomiting, injection site edema raised 1 mm or greater, and headache
- Most common adverse reactions reported in pediatric patients were nausea, hypoglycemia, vomiting, headache, abdominal pain, hyperglycemia, injection site discomfort and reaction, and urticaria
- Patients taking concomitant beta-blockers may have a transient increase in pulse and blood pressure. In patients taking concomitant indomethacin, GVOKE may lose its ability to raise glucose or may produce hypoglycemia. GVOKE may increase the anticoagulant effect of warfarin
Please see full Prescribing Information for GVOKE.